We have Started From A Formal Description Of Android Application Development ..Then After We Had Learned About How To Configure Your System With Eclipse To Develop Your Android Apps..Then We Learned About How To Setup Android Virtual Device To Test Our Android Applications..
If You Didn’t Read My Last Articles On these..Its Highly Recommended To Go Through That Articles..
If You Didn’t Read My Last Articles On these..Its Highly Recommended To Go Through That Articles..
Anyways So
finally we are now ready to build our first android app. usually you start with
“hello world” program as your first
program in any programming language but here let’s start with something new and
a small app that uses a button which when clicked shows a message . Here you are
going to learn how to use button, edit text and give background to your app in
xml file. Before you start developing this app its necessary to know about the
project structure.
Here is how a project structure tree looks when you create
an Android project.
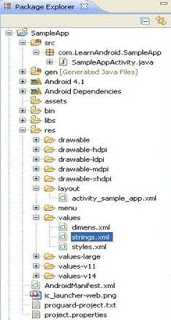
The brief description of important
files/folders in the Android project structure is as follows
files/folders in the Android project structure is as follows
/SRC
The src folder contains the
Java source code files of your application organized into packages. You can
have more than one package in your Android application. Its always a good
practice to break the source code of your application into different packages
based on its core functionality. All the source files of your Activities,
Services etc. Goes into this folder. In the above screen, you can see the
source file of the Activity that we created for our project.
Java source code files of your application organized into packages. You can
have more than one package in your Android application. Its always a good
practice to break the source code of your application into different packages
based on its core functionality. All the source files of your Activities,
Services etc. Goes into this folder. In the above screen, you can see the
source file of the Activity that we created for our project.
/GEN
The files in the gen folder
are automatically generated by the ADT. Here the R.java file contains
reference/index to all the resources in the res we use in our
program. Each time we add a new resource to the project, ADT will automatically
regenerate the R.java file containing reference to the newly added
resource. You should not edit the contents of R.java file manually or
otherwise your application may not compile.
are automatically generated by the ADT. Here the R.java file contains
reference/index to all the resources in the res we use in our
program. Each time we add a new resource to the project, ADT will automatically
regenerate the R.java file containing reference to the newly added
resource. You should not edit the contents of R.java file manually or
otherwise your application may not compile.
/ANDROID
<version number>
<version number>
This folder is also called Android
target library in Android project structure. The version number will be same as
the build target version that we choose while creating a new project.
The android.jar file contains all the essential libraries
required for our program.
target library in Android project structure. The version number will be same as
the build target version that we choose while creating a new project.
The android.jar file contains all the essential libraries
required for our program.
/ASSETS
The assets folder is used to
store raw asset files. You can keep any raw data in the assets folder and
there’s an asset manager in Android to read the data stored in the folder. The
raw data can be anything such as audio, video, images etc. On important point
about assets folder is that the data stored in this folder can’t be referenced
by an ID. To access a data in this folder, we have to work with bits and bytes.
store raw asset files. You can keep any raw data in the assets folder and
there’s an asset manager in Android to read the data stored in the folder. The
raw data can be anything such as audio, video, images etc. On important point
about assets folder is that the data stored in this folder can’t be referenced
by an ID. To access a data in this folder, we have to work with bits and bytes.
/BIN
/bin folder is where our compiled application files go. When we
successfully compile an application, this folder will contain java class files,
dex files which are executable under Dalvik virtual machine, apk archives etc.
successfully compile an application, this folder will contain java class files,
dex files which are executable under Dalvik virtual machine, apk archives etc.
/RES
Res folder is where we store all our external resources for our
applications such as images, layout XML files, strings, animations, audio files
etc.
applications such as images, layout XML files, strings, animations, audio files
etc.
Sub folders:
/res/drawable
This folder contains the bitmap file
to be used in the program. There are three different folders to store
drawables. They are drawable-ldpi, drawable-mdpi, and drawable-hdpi. The
folders are to provide alternative image resources to specific screen
configurations. Ldpi, mdpi & hdpi stands for low density, medium density
& high density screens respectively. The resources for each screen
resolutions are stored in respective folders and the android system will choose
it according to the pixel density of the device.
to be used in the program. There are three different folders to store
drawables. They are drawable-ldpi, drawable-mdpi, and drawable-hdpi. The
folders are to provide alternative image resources to specific screen
configurations. Ldpi, mdpi & hdpi stands for low density, medium density
& high density screens respectively. The resources for each screen
resolutions are stored in respective folders and the android system will choose
it according to the pixel density of the device.
/res/layout
An XML file that defines the User
Interface goes in this folder.
Interface goes in this folder.
/res/values
XML files that define simple
values such as strings, arrays, integers, dimensions, colors, styles etc. are
placed in this folder.
values such as strings, arrays, integers, dimensions, colors, styles etc. are
placed in this folder.
/res/menu
XML files that define menus in your
application go in this folder
application go in this folder
Android
Manifest file
Manifest file
AndroidManifest.xml is one of the most important file in the Android project
structure. It contains all the information about your application. When an
application is launched, the first file the system seeks is the Android
Manifest file. It actually works as a road map of your application, for the
system.
structure. It contains all the information about your application. When an
application is launched, the first file the system seeks is the Android
Manifest file. It actually works as a road map of your application, for the
system.
The Android Manifest file contains
information about:
information about:
- Components of your application such as Activities,
services etc. - User permissions required
- Minimum level of Android API required
Finally done with lots of reading of Project Structure Tree it’s time
to try out your first app.
to try out your first app.
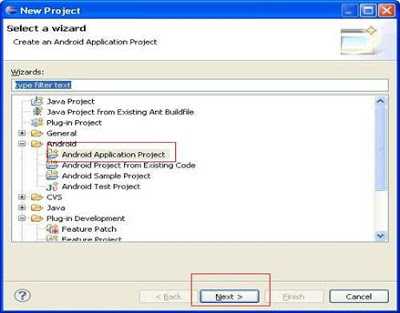
Step 1: Go to file -> New -> project->Expand Android And Select Android Application Project
Step 2- Choose the lowest version
API level in “minimum Required SDK” if you installed any lower version below
API 16 because an app build on lower version API always supported by their
successive higher version.
API level in “minimum Required SDK” if you installed any lower version below
API 16 because an app build on lower version API always supported by their
successive higher version.
Remember here you can only deploy your app on Android
4.1 as you set the target so.
4.1 as you set the target so.
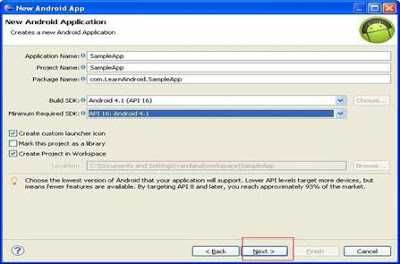
Step 3- After entering all the details as above you can see
the next screen in which you can change the background, foreground color and
image etc only if you want and click next.
the next screen in which you can change the background, foreground color and
image etc only if you want and click next.
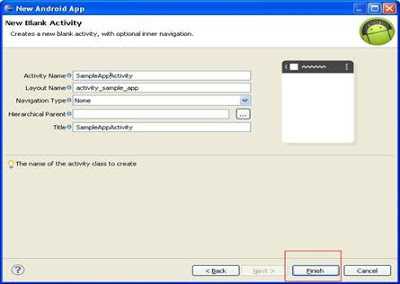
Step 4- Here you can change
the activity name which is going to display in your tiltle of your app
bydefault it displays MainActivity but I changed it to the app name i.e.,
SampleAppActivity (naming convention is same as used in java) then click finish
.
the activity name which is going to display in your tiltle of your app
bydefault it displays MainActivity but I changed it to the app name i.e.,
SampleAppActivity (naming convention is same as used in java) then click finish
.
Its going to create a SampleAppActivity java file ,activity_sample_app
xml file and other folders and files which you can check out in the package
explorer the screen shot of which is already described in project tree
structure.
Here is how your SampleAppActivity
java file bydefault looks –
java file bydefault looks –
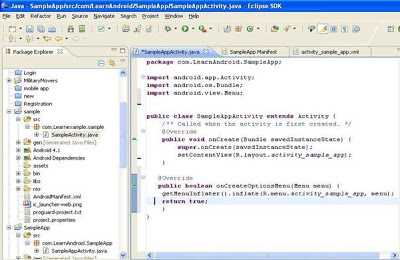
The basic unit
of an Android application is an Activity. An Activity
displays the user interface of your application, which may contain widgets like
buttons, labels, text boxes, etc. Typically, you define your UI using an XML
file .For example, the activity_sample_app
xml.xml file located in
the res/layout folder, which may
look like this (bydefault) –
of an Android application is an Activity. An Activity
displays the user interface of your application, which may contain widgets like
buttons, labels, text boxes, etc. Typically, you define your UI using an XML
file .For example, the activity_sample_app
xml.xml file located in
the res/layout folder, which may
look like this (bydefault) –
<?xml
version=”1.0″ encoding=”utf-8″?>
version=”1.0″ encoding=”utf-8″?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
xmlns:tools=”http://schemas.android.com/tools”
android:layout_width=”match_parent”
android:layout_height=”match_parent”
>
>
<TextView
android:layout_width=”wrap_content”
android:layout_height=”wrap_content”
android:layout_centerHorizontal=”true”
android:layout_centerVertical=”true”
android:padding=”@dimen/padding_medium”
android:text=”@string/hello_world”
tools:context=”.MainActivity”
/>
/>
</RelativeLayout>
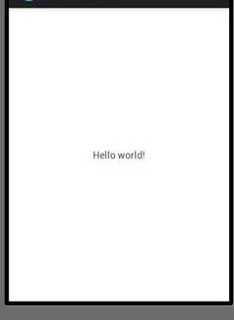
When
you run the following code you can get to see the following screen on your
emulator
you run the following code you can get to see the following screen on your
emulator
Now in order to develop the app as required we need to edit
these two files. Just edit as explained below:
these two files. Just edit as explained below:
Switch back to activity_sample_app xml file and edit as follows or simply copy the below
code.
code.
1. <?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”utf-8″?>2. <RelativeLayout
3.
xmlns:android=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”4. xmlns:tools=”http://schemas.android.com/tools“5.
android:layout_width=”match_parent”6.
android:layout_height=”match_parent”7.
android:background=”@drawable/image” >8.9. <TextView10. android:id=”@+id/textView1″11. android:layout_width=”wrap_content”12. android:layout_height=”wrap_content”13. android:layout_alignParentLeft=”true”14. android:layout_centerVertical=”true”15. android:gravity=”left”16. android:padding=”@dimen/padding_medium”17. android:text=”@string/hello_friends”18. android:textColor=”@color/turquoise”19. android:textSize=”35dp”20.
android:textStyle=”italic”21. android:typeface=”serif”
/>22.23. <Button24. android:id=”@+id/button1″25. android:layout_width=”wrap_content”26. android:layout_height=”wrap_content”27. android:layout_alignParentBottom=”true”28.
android:layout_alignParentLeft=”true”29. android:layout_marginBottom=”24dp”30. android:layout_marginLeft=”18dp”31. android:background=”@drawable/img”32. android:text=”@string/Go”33. android:textStyle=”italic” />34.35.
</RelativeLayout>
Now
open
SampleAppActivity java file and add the code((the bold lines are added) or else copy
the code. (Don’t Copy The Line Numbers With Code)
open
SampleAppActivity java file and add the code((the bold lines are added) or else copy
the code. (Don’t Copy The Line Numbers With Code)
1. package com.LearnAndroid.SampleApp;
2. import android.app.Activity;3. import android.os.Bundle;4. import android.view.View;5. import android.view.View.OnClickListener;6. import android.widget.Button;7. import android.widget.Toast;8. public class SampleAppActivity extends Activity {9. /** Called when the
activity is first created. */10. @Override11. public void
onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {12.
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);13.
setContentView(R.layout.activity_sample_app);14. Button button = (Button)
findViewById(R.id.button1);15. button.setOnClickListener(new
OnClickListener() {16. @Override17. public void onClick(View v) {18.
Toast.makeText(SampleAppActivity.this, “Welcome To The World Of
Android”, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();19. }20. });21. }22.
}
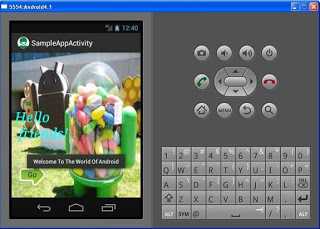
That’s it you are now ready to run your first app. There
are many ways to run the app. Just right click on the SampleApp in the package
explorer you have created then Run As android application. Check out the screen
shot below to run!
are many ways to run the app. Just right click on the SampleApp in the package
explorer you have created then Run As android application. Check out the screen
shot below to run!
Please wait for a while it takes few
minutes to deploy it in the emulator and when it loads voila! You have created
your first app.
minutes to deploy it in the emulator and when it loads voila! You have created
your first app.
Enjoy!!